Ottawa Hospital is transforming how its clinical teams work and interact with patients using a cutting-edge AI ambient voice solution known as Microsoft DAX Copilot. After adopting this technology, the hospital observed up to a 70% reduction in clinician-reported burnout and saw patient satisfaction rates climb near 97%. These results have positioned Ottawa Hospital at the forefront of AI-driven healthcare innovation in Canada, especially in its collaboration with Microsoft and Epic.
Deploying AI to ease administrative burdens and boost quality of care is becoming standard for leading hospitals. For Ottawa Hospital, the integration of these systems is more than a tech upgrade – it’s a shift in how care is delivered and experienced by both physicians and patients.
AI Voice Tools Changing Healthcare Workflows
The role of AI voice capture tools in healthcare operations has quickly expanded, addressing long-standing challenges like physician burnout and documentation overload. In many facilities, administrative tasks, charting, and recordkeeping keep clinicians late after hours.
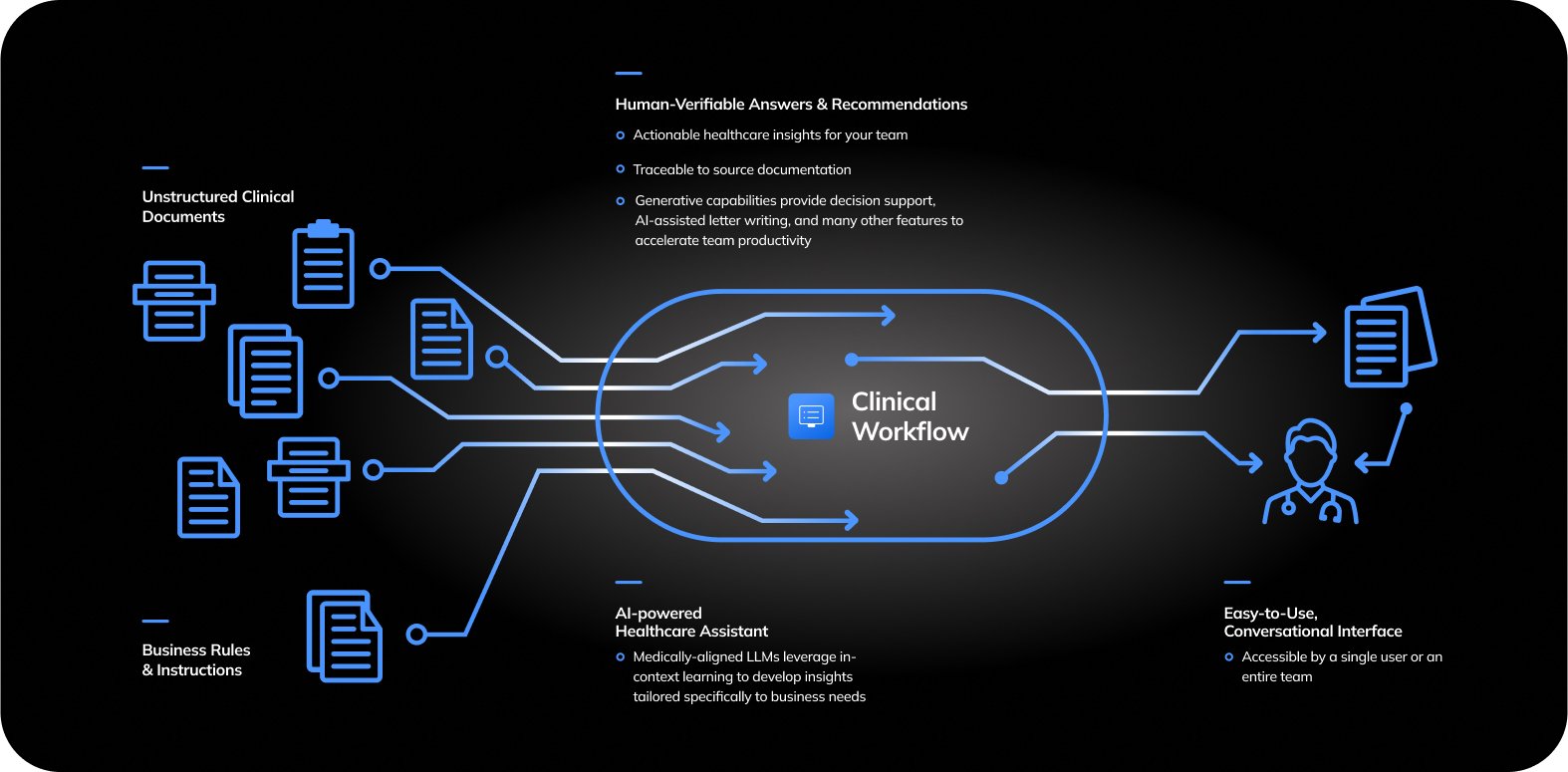
With AI voice assistants, the manual side of transcribing notes and updating health records is greatly reduced. The AI records the consultation, then extracts key details such as symptoms, diagnosis, and suggested treatment plans and instantly uploads them into the electronic health record (EHR).
Clinicians are reporting that this technology not only frees up more time for direct patient care but also lessens their cognitive load during each appointment. Instead of focusing on typing or clicking through paperwork, providers can concentrate fully on their patient. Efficiency is up, and the workflow feels more natural and human-focused, improving morale among staff.
Hospitals are now able to see more patients and cut down on administrative bottlenecks. This shift doesn’t just impact hospital finances – it changes how patients and providers interact at every level.
How Ottawa Hospital Adopted Microsoft DAX Copilot
Ottawa Hospital was the first in Canada to pilot Microsoft’s DAX Copilot. The tool captures real-time conversations between clinicians and patients, then drafts clinical notes – dramatically slashing time spent on clerical work. Early in the rollout, Ottawa Hospital set up a detailed evaluation framework to measure the tool’s impact and guide refinement.
Leadership at Ottawa Hospital worked closely with Microsoft and Epic to integrate the technology into daily operations. This was not a plug-and-play transition; it involved regular training, ongoing technical support, and continuous communication with staff. Important feedback mechanisms were put in place, such as monthly updates through Microsoft Power BI dashboards that incorporated insights from clinicians, surveys, and EHR data.
This strategic adoption allowed Ottawa Hospital to scale up its pilot program rapidly, ensuring that all physician categories could benefit. Management also emphasized the need for strong clinical governance throughout, ensuring healthcare standards weren’t compromised during the transition to this new digital workflow.
By focusing on collaboration and not just deployment, the hospital made certain the technology fit seamlessly within clinical routines and supported the goals of both doctors and patients.
The success of DAX Copilot in Ottawa is already serving as a model for other organizations considering AI-driven clinical transformation in healthcare settings.
Integration with Epic and AI-Driven Note Taking
A key aspect of Ottawa Hospital’s approach has been the direct integration of DAX Copilot with Epic, their main EHR platform. By doing so, clinicians don’t need to learn a brand-new system – all AI-generated notes appear natively in their regular workflow.
Via a mobile app, clinicians start recording – the AI passively listens as the interaction unfolds. After the visit, the draft note is ready for quick review and approval by the doctor, rather than painstaking manual entry. The key benefits here? No time wasted, improved note quality, and fewer after-hours charting tasks.
Epic’s secure environment ensures that all these notes, and the entire process, meet data integrity and confidentiality standards. Doctor-patient conversations are transcribed and formatted to match each specialty’s needs, reflecting the complexity and specificity required in modern healthcare documentation.
While the system is working in the background, clinicians can stay focused on patient care, leaving only minimal corrections or additions to the AI’s draft. This approach raises the documentation baseline and supports clinical thoroughness without loss of physician attention or quality of care.
Measuring Impact: Physician Time Savings and Burnout Reduction
Ottawa Hospital carefully tracks the impact of DAX Copilot on both staffing and patient outcomes. Clear metrics are reported: On average, seven minutes are saved for every patient encounter. Multiply that across dozens of daily appointments, and the time-saving is substantial for the clinical teams.
The Canadian Medical Association points out that physicians normally spend around 10 hours per week just on administrative tasks. With DAX Copilot, this time is being cut dramatically, enabling more face-to-face time with patients and giving staff back precious hours in their day.
Feedback from clinicians highlights two core improvements:
- Marked reduction in after-hours documentation
- Significantly less cognitive fatigue at the end of shifts
For many, these improvements have changed both job satisfaction and work-life balance. By automating repetitive charting and freeing up clinicians to focus on clinical judgment and patient care, the hospital is not just improving operational metrics – it’s taking direct aim at the issue of doctor burnout, a top concern in many modern health systems.
This change in workload has also been linked to improved team morale and a reduction in errors or missed documentation, providing long-term benefits well beyond immediate time savings.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction Rates
Patient satisfaction is a main focus for Ottawa Hospital’s rollout of AI tools. Surveys show that 93 to 97 percent of patients consider their care at least as good – or better – when DAX Copilot is used during visits. Many report feeling more heard and involved in the consultation process.
This boost in satisfaction is attributed in part to the higher level of engagement from clinicians. With less need to spend time referencing notes or typing on computers, providers are able to give their full attention to patients, creating a more personal and open environment for questions and concerns.
Consent is prioritized. Before any appointment is recorded, patients are informed about the process and given control – either agreeing or declining to participate. Those who consent also gain access to their records directly through the MyChart portal, so they can review what was discussed and clarify follow-up care, further enhancing trust.
Ottawa Hospital’s approach includes strong patient education on how the technology works and how personal data is kept confidential. Transparent communication has made most patients comfortable with the shift to AI-enabled note-taking during medical visits.
This model is already serving as a template for other hospitals considering similar technology, as patient feedback shows clear improvements in both perceived care and the logistics of their healthcare journey.
Privacy, Consent, and Data Security in AI Voice Capture
Ottawa Hospital maintains rigorous data security and privacy protocols around its AI voice capture systems. Each patient is fully informed and must give explicit consent before any recording or AI-driven processing of their consultation.
Notes and recordings are stored securely within the Epic EHR, governed by industry-leading cybersecurity standards. The hospital’s communication materials explain that all recordings remain confidential and are only accessible by the clinical care team and the patient through secure channels.
This emphasis on transparency ensures no patient is surprised by the process, and all have a clear path to opt out if desired. The hospital also provides printed and digital materials outlining the safeguards in place for their health information.
Ottawa Hospital regularly reviews its privacy practices – aligning with Canadian health data laws and international best practices. This ongoing commitment helps maintain public trust, which is crucial in any deployment of AI in healthcare.
AI Model Training and Specialty Customization
DAX Copilot’s success at Ottawa Hospital relies heavily on the continuous training of large language models (LLMs). These models are trained on a vast, curated repository of de-identified clinical data, so the AI understands a huge range of medical situations with strong accuracy and contextual awareness.
Each specialty – emergency, dermatology, cardiology, and more – gets custom model tuning. This means the system produces first drafts that suit the specific terms and workflows of different doctors, reducing the volume of edits needed and keeping all notes relevant and reliable for clinical review.
Microsoft engineers use regular feedback loops, comparing how much clinicians need to edit the AI’s drafts over time. As more data comes in and the model improves, the percentage of text needing manual changes falls, further easing clinicians’ workload.
Tuning also incorporates feedback from Canadian clinicians, ensuring that medical language reflects both global research and local standards of care. This process keeps DAX relevant and practical as deployment expands.
Continuous Feedback and Improvement Loops
Since its launch, Ottawa Hospital has embedded robust feedback mechanisms into its AI integration plan. Monthly analytic reports are generated with Microsoft Power BI, tracking everything from time saved per patient to clinician and patient satisfaction.
Physician and nurse surveys are conducted regularly, with results shared back to hospital leadership and Microsoft for prompt iteration. These insights are vital, not just for identifying problems but also for prioritizing features and improvements that matter most to end users.
Data collected spans technical performance, clinical accuracy, user edits, and the experience of both patients and staff. This broad approach means any pain points or bottlenecks can be quickly addressed in future software updates or workflow changes.
Also Read
Square Enix Symbiogenesis Expands on Sony Soneium Blockchain
By adopting this dynamic improvement strategy, Ottawa Hospital has kept both technology and clinical teams closely aligned, ensuring the tool works well in real-world contexts and adapts as healthcare needs evolve.
Beyond Charting: Future AI Use Cases in Healthcare
While automated charting delivers immediate productivity gains, Ottawa Hospital is already eyeing future applications for their AI voice and assistant systems. Future goals include biomarker detection from patient conversations, earlier identification of health risks, and proactive care interventions rather than just reactive documentation.
Other planned features include automatic post-visit action triggers, like generating order forms, pre-authorizations, and referral letters right after appointments. These changes will allow clinical teams to focus on patient care rather than time-consuming clerical tasks.
There’s also growing interest in using AI as a tool for managing social determinants of health, picking up on factors that might not be obvious during short in-person visits but could have a major impact on patient outcomes. This includes anything from housing security to transportation access.
Also Read
Last Chance to Exhibit at TechCrunch AI Sessions at Berkeley
As AI models mature, these use cases will help shift healthcare toward a more holistic and continuous care model where interventions happen sooner, and patients get more personalized support at every stage of their treatment.
Digital Avatars and AI Teammates in Hospitals
Ottawa Hospital has moved beyond traditional AI tools by piloting “digital teammates” like their multilingual avatar, Sophie. Developed in partnership with Deloitte, Sophie can communicate in several languages, interpret patient sentiment and even detect when verbal reports don’t match physical indicators of pain or discomfort.
These avatars can engage with patients more conversationally, asking clarifying questions or guiding them through next steps in their healthcare journey – something especially helpful for those who struggle with language barriers or medical terminology.
The hospital is preparing to launch more avatars in the future, including those designed to support patient navigation, handle pre-screening, and improve access to care resources. This approach makes tech more approachable, blending human warmth with high-tech precision.
Also Read
Florida Encryption Backdoor Bill for Social Media Fails to Pass
Sophie and future avatars are designed to identify patient needs before they escalate and connect them to the right resources quickly, all while maintaining empathy and supporting staff in routine interactions.
Addressing Staffing Shortages with AI Assistants
Staffing shortages are top of mind for healthcare leaders globally, and Ottawa Hospital is no exception. AI tools like digital avatars and automated follow-up systems are being deployed to support overextended human staff, maximizing the number of patients who get post-visit calls or check-ins.
For high-volume procedures, avatars can confirm discharge instructions, assess medication compliance, and clarify next steps – even escalating to human physicians or nurses if any answers fall outside safe parameters. This ensures every patient receives essential follow-up support, regardless of clinic workload.
By shifting clerical and low-risk patient communication to AI-powered teammates, hospitals make the most of limited clinical resources, allowing the most skilled practitioners to prioritize urgent or complex needs. Patients experience a more consistent level of contact, while staff can focus on their core strengths and direct care activities.
Also Read
Apple’s New Chips Target Smart Glasses, Macs, and AI Hardware
Real World Outcomes and Staff Reactions
Clinician feedback at Ottawa Hospital has been overwhelmingly positive. Many physicians and nurses say the tool gives them “their time back” and reduces stress at the end of each day. Less time spent on paperwork, combined with higher quality notes, supports better medical outcomes and stronger job satisfaction.
Some clinicians have noted initial skepticism, especially regarding relying on AI for medical records, but user-friendly design and responsive support helped ease the transition. Input from staff during the early stages was essential in refining the interface and minimizing friction in adoption.
Patients, too, have expressed greater satisfaction with the level of attention and explanation during their consultations. With less time spent on back-office tasks, clinical teams have more energy for face-to-face interaction and listening, making each visit more meaningful.
Early results suggest that these workplace improvements are also associated with lower error rates and more accurate recordkeeping. This feedback creates a positive feedback loop – driving adoption and continuous improvement for the AI tools.
Also Read
Widespread Timeline Issues Hit X as Users Report Outages
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Clinical Settings
Even with careful planning, AI integration in hospitals is not without its challenges. Data security and privacy must remain a top concern – both because of regulatory standards and to maintain public confidence.
Some clinical specialties require highly nuanced documentation or deal with complex cases that are harder for even advanced AI to summarize accurately. For these areas, ongoing tuning and clinician oversight are essential to avoid errors or omissions.
Patient openness isn’t universal. While most have responded positively, a minority have expressed concerns over being recorded or prefer traditional note-taking. Ottawa Hospital addresses this with clear consent protocols and the ability to opt-out, but it highlights the need for continued patient education.
Another challenge is ensuring the AI’s language and recommendations stay up to date with changing medical guidelines and evolving local standards of practice. Interdisciplinary review and targeted model retraining are part of the hospital’s ongoing quality assurance plan.
Also Read
Zen Agents by Zencoder: Team-Based AI Tools Transform Software Development
What’s Next for AI Ambient Voice in Healthcare?
Looking ahead, Ottawa Hospital aims to expand its use of AI voice tools beyond routine charting and documentation. Integration with more hospital workflows and linking AI outputs with actionable care plans will create even greater efficiency and personalized support for both patients and clinical teams.
Planned developments include better integration of avatars within the EHR itself, more sophisticated real-time analytics, and potential expansion of AI summaries to support other roles such as nursing, care coordinators, and specialists.
The ultimate goal is to harness AI not just for administrative relief, but to move closer to proactive, preventive, and patient-centered care. As the technology evolves and proves its value, Ottawa Hospital’s pioneering work will continue to shape the next generation of healthcare delivery.