CoreWeave, a New Jersey-based data center operator, is seeking a $1.5 billion debt deal as its recent IPO underperformed. The company just went public in March 2025, targeting a $2.7 billion fundraise, but ended up slashing that goal by almost half amid investor hesitation and mounting borrowing costs.
This move follows a period where CoreWeave expanded quickly to support the booming growth of AI infrastructure, budgeting massive funds for data center buildouts. The pressure from previous debts and a cooling in the AI market are now pushing the company to seek fresh capital to stabilize its operations.
CoreWeave’s Debt Roadshow
CoreWeave organized a roadshow this week in partnership with bankers at JPMorgan. The main goal is to present the company’s current debt situation and future plans directly to potential investors, hoping to spark enough interest to secure the financing required.
During these meetings, executives are expected to share details about the company’s liabilities, projected revenues, and anticipated growth trajectory in AI infrastructure services. By explaining their roadmap and repayment plans, CoreWeave aims to address concerns about its financial structure.
A successful roadshow is critical, as failing to secure favorable terms could lead to tighter budgets, possible project delays, or the need for additional restructuring. The meetings will serve as a pulse check for investor trust and confidence in the company’s new direction after its IPO faced setbacks.
This type of high-profile debt syndication is now seen as a necessary step as market conditions have become less forgiving for heavily leveraged tech ventures aiming to scale aggressively.
Investors will be watching to see whether the company can strike a balance between liabilities and driving innovation in the AI sector.
Why the IPO Disappointed
CoreWeave’s IPO in March was closely watched, with initial expectations that it would bring in up to $2.7 billion. However, concerns over the company’s significant debt load, and a shifting investor mood around large capital-intensive tech, led to lowered demand.
The fundraising target was eventually cut to $1.5 billion, matching the amount the company is now trying to secure through debt. This significant adjustment underlines how quickly investor sentiment changed and how much scrutiny CoreWeave’s finances have come under.
Some investors were turned off by the volume of existing debt on CoreWeave’s books, questioning its ability to handle future repayments. Weakness in the broader market for AI infrastructure further cooled excitement for the IPO, leading to soft pricing and limited demand in secondary markets once shares began trading.
Even with customers like Microsoft, the company’s exposure to AI trends that can move rapidly up or down makes stability harder to predict for prospective shareholders and creditors.
AI Infrastructure Market Slowdown
After several years of intense growth, the AI infrastructure market has started to cool. Spending across the sector surged from 2021 as companies scrambled to build or upgrade data centers for machine learning and cloud workloads. But in late 2024 and early 2025, demand growth began to slow.
For infrastructure providers like CoreWeave, this means tougher competition for new contracts and more pressure to show profitability rather than just expansion. Market analysts point out that recent macroeconomic trends, including higher interest rates and more cautious capital flows, have made major investments harder to justify for companies and customers.
AI research continues to advance, but budget cycles among the biggest tech clients can fluctuate. Customers are more careful with procurement of large-scale compute power, waiting to see which providers can offer the best mix of reliability, cost, and service.
The shift has left firms that grew too quickly at risk of overextending, especially if their funding assumptions no longer match today’s reality. For CoreWeave, scaling back fundraising goals and seeking new debt is a direct response to this changed landscape.
CoreWeave’s Debt History
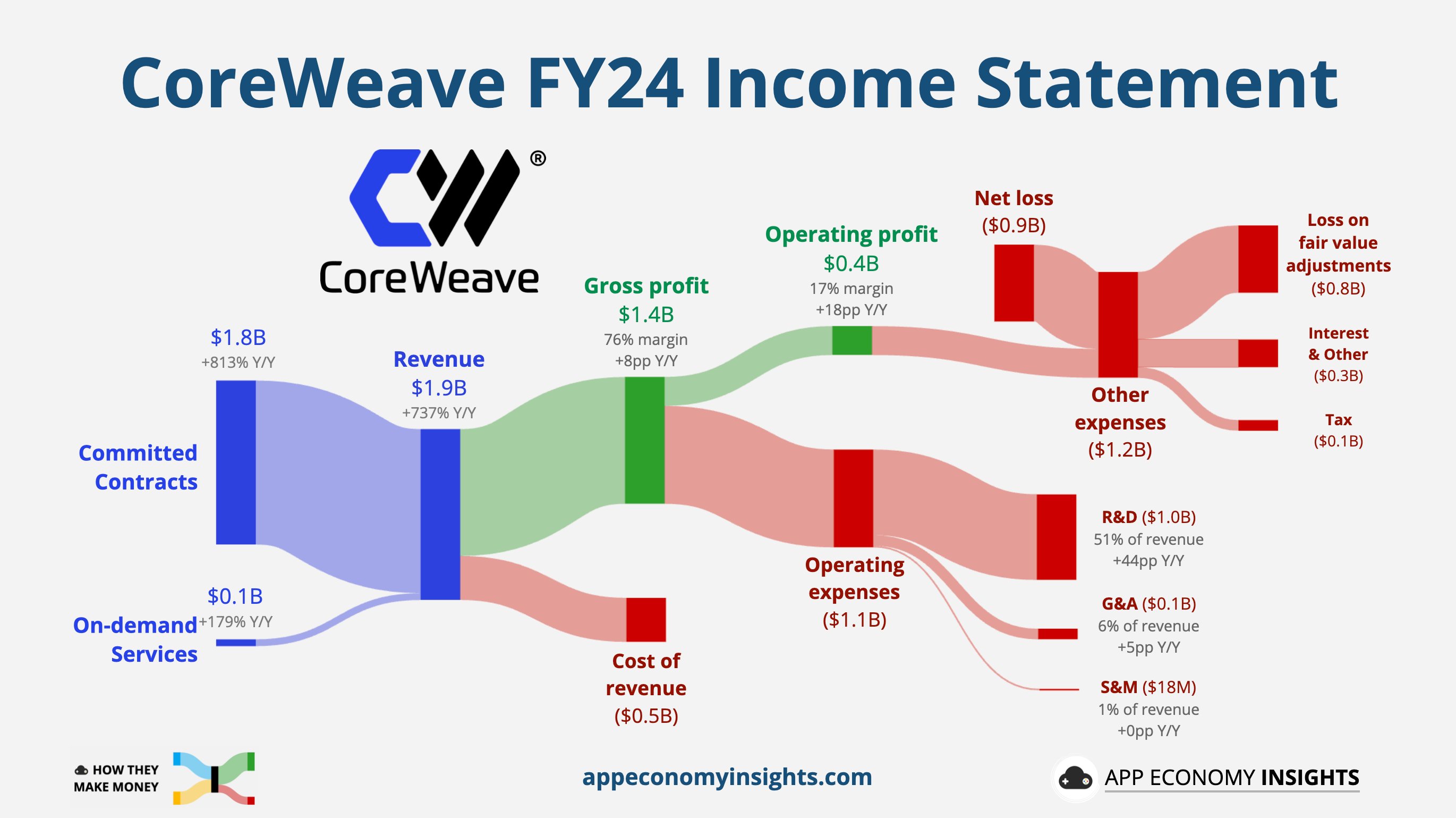
Since 2023, CoreWeave raised approximately $12.9 billion in debt to fund its data center expansion. The bulk of this occurred during a period of aggressive growth, as the company aimed to support the surging needs of machine learning and data analytics workloads from enterprise clients.
Also Read
Square Enix Symbiogenesis Expands on Sony Soneium Blockchain
By December 2024, CoreWeave’s balance sheet showed around $8 billion in total debt. Much of this came from loans, bonds, and structured deals with major banks. The easy access to capital allowed rapid facility construction but also left the company vulnerable to changing financial conditions.
The scale of borrowing is significant even by tech standards. This aggressive leverage was justified by executives with projections of future revenues from fast-growing AI demand. However, now that the market has cooled and cash flow takes center stage, investors are focused on how the company will manage and eventually reduce its debt.
Debt Pressure and Deadlines
One of CoreWeave’s most urgent challenges is the coming deadline for major repayments. The Financial Times reports that the company faces required debt and interest payments of $7.5 billion by the end of 2026.
This looming obligation increases urgency for CoreWeave to either refinance, extend debt maturities, or generate enough cash flow to avoid financial strain. This payment pressure is influencing every aspect of the company’s operations, from project spending to hiring to partner agreements.
Also Read
Florida Encryption Backdoor Bill for Social Media Fails to Pass
Executives are under pressure to convince lenders and credit analysts that the company has a realistic path to meeting its obligations. Potential outcomes include asset sales, new partnerships, or renegotiating payment terms to buy time in a difficult funding environment.
If CoreWeave is unable to restructure or refinance these obligations, there is a risk that operations may be disrupted or, in a worst-case scenario, that some assets might need to be divested to pay off creditors.
Major Customers and Partnerships
CoreWeave boasts a roster of significant clients, including Microsoft, which relies on the company’s data center resources to power large-scale cloud and AI applications. These relationships provide a measure of stability and recurring revenue that is critical for CoreWeave’s financial forecasting.
Such partnerships have historically helped CoreWeave secure financing during expansion phases, as they show a clear pathway from infrastructure investment to revenue. Investors look closely at these ties to evaluate the long-term commercial viability of the company, especially in a competitive sector.
Also Read
Apple’s New Chips Target Smart Glasses, Macs, and AI Hardware
Besides Microsoft, CoreWeave works with a variety of cloud-first startups, SaaS providers, and research organizations that need high-compute environments. These deals allow CoreWeave to showcase its technical strengths and network reach.
The strength and visibility of these partnerships will likely be a key discussion point during the debt roadshow and future investor talks, influencing how lenders view the company’s ability to weather a changing tech market.
Reactions from Investors and Banks
The investor response to CoreWeave’s post-IPO financing strategy has been mixed. While some backers recognize the long-term potential in the AI infrastructure market, many are wary of the company’s current leverage and unproven ability to self-fund growth.
Banks such as JPMorgan are helping lead the debt process, seeking ways to structure deals that protect lenders while giving CoreWeave room to adjust. Some existing creditors may push for stricter covenants or higher interest rates to offset perceived risk.
Also Read
Widespread Timeline Issues Hit X as Users Report Outages
Investor discussions reportedly focus on transparency, business maturity, and near-term profitability. Major institutional investors, who typically buy corporate debt, want clarity on exactly how CoreWeave plans to avoid additional fundraising setbacks in the next 24 months.
The outcome of these talks will set a tone for how other new tech players manage similar challenges in the evolving data infrastructure landscape.
Data Center Expansion Challenges
Rapid data center construction is expensive and logistically demanding. CoreWeave faced challenges common to the industry, such as delays in supply chain, securing land and utilities, and rising costs for energy and specialized talent.
The firm’s accelerated expansion exposed it to timing risks as the market cooled faster than anticipated. Now, the challenge is to optimize its large fleet of infrastructure while ensuring each site meets utilization and profitability targets.
Also Read
Zen Agents by Zencoder: Team-Based AI Tools Transform Software Development
Balancing expansion and operational efficiency is a key hurdle for CoreWeave’s management team. Making underutilized capacity profitable, or scaling back non-essential spending, could prove essential in the coming years as debt repayments become due.
Furthermore, competitors with more conservative investment strategies may be better positioned to adapt quickly to shifts in data workload demand, placing extra competitive pressure on CoreWeave.
Impact on AI and Cloud Markets
What happens with CoreWeave’s finances and operations will ripple across the broader AI and cloud infrastructure markets. As one of the fastest-growing independent players, CoreWeave’s trajectory is closely monitored by analysts and rivals alike.
If it succeeds in meeting obligations and staying innovative, CoreWeave’s story will reinforce the importance of strong partnerships and transparent financial planning in the new AI economy. On the other hand, struggles or failed restructuring could make lenders more conservative about backing other ambitious tech infrastructure projects.
Also Read
Google Partners with Elementl Power to Develop 1.8 GW Advanced Nuclear for Data Centers
The results may impact customers’ ability to secure affordable AI compute power, influence pricing structures across the cloud industry, and accelerate or slow the rollout of next-generation AI platforms.
CoreWeave’s journey is a case study in the risks and rewards of aggressive expansion during a technology boom, and the crucial role of financial discipline as markets mature.